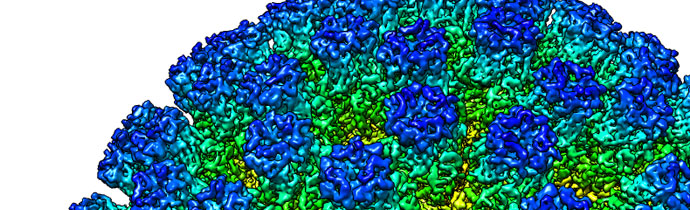
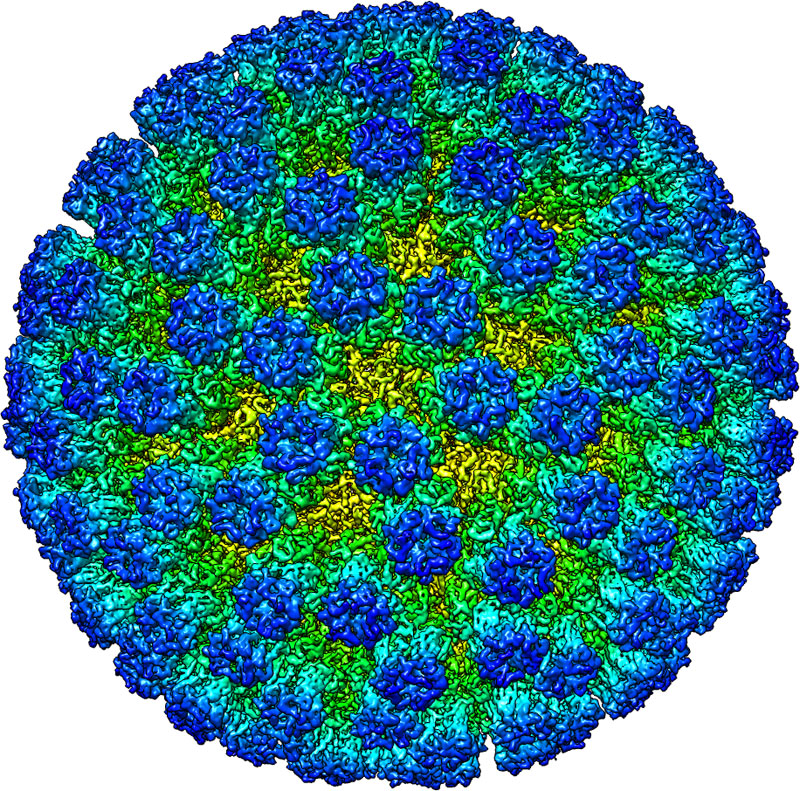
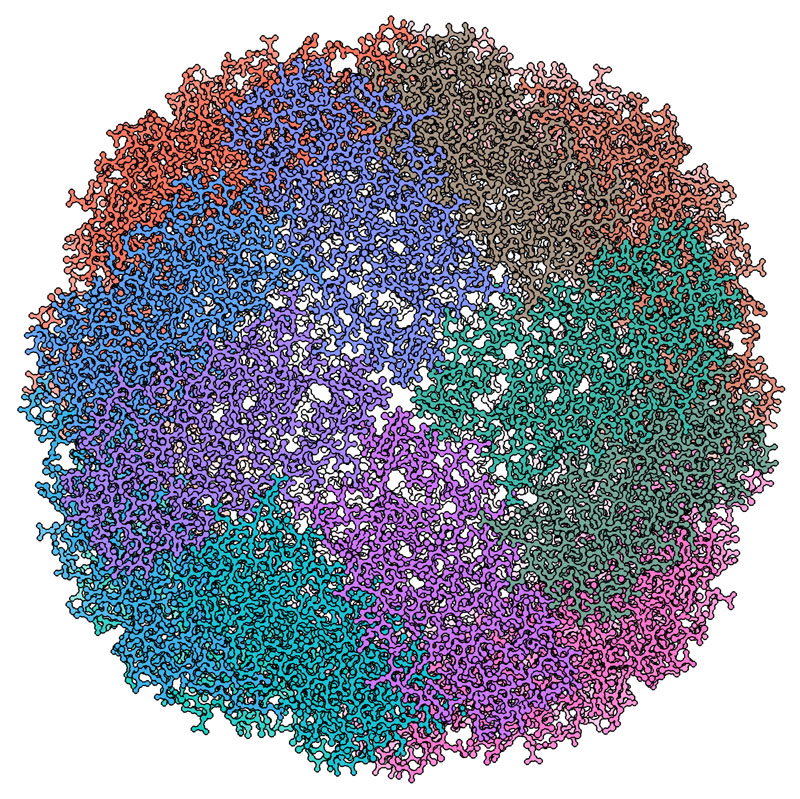
Cryo-EM in Structural Biology
With Cryo-EM you can study samples in their natural state at atomic resolution. Here’s an overview of how it’s used in structural biology for studying viruses, organelles, proteins and molecular interactions at a resolution not possible just a few years ago.
Blue Scientific is the official distributor for Gatan TEM/SEM cameras, filters and sample preparation systems in Norway, Sweden, Denmark, Finland and Iceland. For more information or quotes, please get in touch.
Gatan systems
More about cryo-EM
Contact us on +44 (0)1223 422 269 or info@blue-scientific.com
Follow @blue_scientificCryo-EM
Single-particle cryo-electron microscopy is an increasingly popular method for solving structures at atomic resolution. It enables you to study frozen-hydrated samples in vitreous (non-crystalline) ice. This maintains the ultra-structure, buffer and ligand distribution in its natural state.
In structural biology, cryo-EM is used to study:
- Viruses
- Small organelles
- Macromolecular biological complexes
- Purified proteins
- Molecular interactions in supramolecular assemblies or machines
In single-particle cryo-EM, a TEM (Transmission Electron Microscope) is used to record high resolution images of thousands to hundreds of thousands of identical, but randomly oriented, particles (molecules) from each specimen. These images are then grouped, aligned and averaged using image classification algorithms to distinguish between multiple orientations of the 3D molecule.
With the right sample, cryo-EM can solve molecular structures at a resolution below 1.5 Å. This level of resolution level was inconceivable just a few years ago.
Courtesy of Kato T, Makino F, Nakane T, Terahara N, Namba K. Osaka University.
In 2017 the Nobel Prize for Chemistry was awarded to Jacques Dubochet, Joachim Frank and Richard Henderson for “developing cryo-electron microscopy for the high-resolution structure determination of biomolecules in solution”. Details are on the Nobel Prize website.
More about the cryo-EM…Cryo-EM in Structural Biology
Structural biology involves studying the mechanisms and interactions of partner molecules in biological or disease processes. Cryo-electron microscopy enables you to:
- Obtain structural information without crystallising target proteins
- Image protein complexes and protein-ligand interactions
- Study macromolecules in as close to a natural state as possible
- Identify and characterise dynamic biological states by observing multiple conformations.
Antibodies and Vaccine Research
With cryo-EM you can map interactions between antibodies and antigens in biological drug and vaccine design studies. You can routinely achieve near-atomic resolution structures of entire viruses and virus-like particles.
Mapping the coronavirus structure with cryo-EM
Characterise Nanotechnology / Drug Delivery Systems
Cryo-EM provides structural information about samples in a condition close to their native state. This is useful in development and manufacturing programmes for the design of new drug delivery systems including liposomes and dendrimers.
You can also elucidate structure-function relationships during the design of macromolecular-based nanotech devices.
Drug Discovery / Rational Design
Near-atomic resolutions can be readily achieved using cryo-EM. This reveals not only the presence of compounds and their protein targets, but also the mechanisms that bind them. This is extremely useful in pharmaceutical R&D, for studying the structures of proteins that are difficult to crystallise. You can investigate membrane proteins of therapeutic interest, such as channels and receptors.
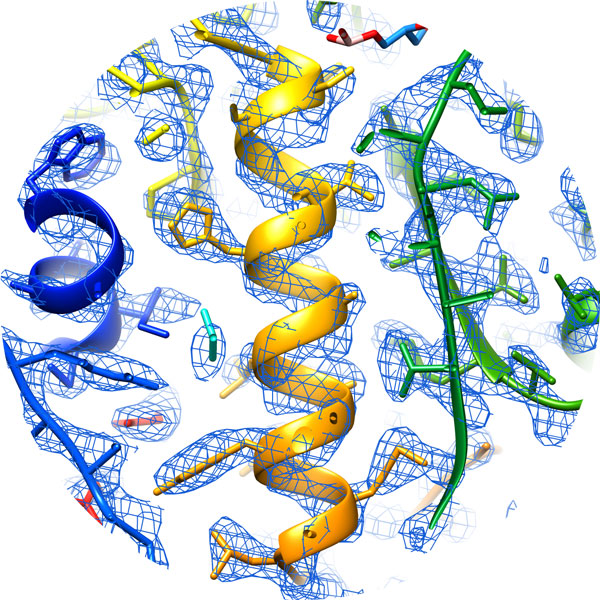
Cryo-EM Featured on BBC Science
Cryo-EM has been featured this week on on BBC Science, with striking comparisons of images from previous techniques compared with today’s technology.
Read the article on BBC ScienceWhat is ‘blobology’ and how is it transforming biology? https://t.co/vq2WmUaJ2F pic.twitter.com/zEvFrrI1Lp
— BBC Science (@BBCScienceClub) August 21, 2019

Instrumentation: Gatan K3 Camera
Next generation direct detection camera for electron microscopes, ideal for cryo-EM.
- Low dose for beam-sensitive materials
- Large field of view
- 1,500 frames per second
Cryo-EM at Diamond Light Source
Diamond Light Source have opened a centre offering cryo-EM services to the global pharmaceutical and biotech industry called eBIC for Industry (eBIC = electron Bio-Imaging Centre) incorporating a UK National Center for cryo-electron microscopy.
The centre provides access to state-of-the-art microscopes, experienced specialists and complementary synchrotron-based techniques.
More about the centreMore Information
If you’d like any more information about using cryo-EM for your research, to how to implement it in your lab, just get in touch.
Blue Scientific is the official Nordic distributor of Gatan TEM/SEM cameras, filters and sample preparation systems. We’re available to answer all your questions:
Contact us on +44 (0)1223 422 269 or info@blue-scientific.com
Gatan systems for TEM/SEM
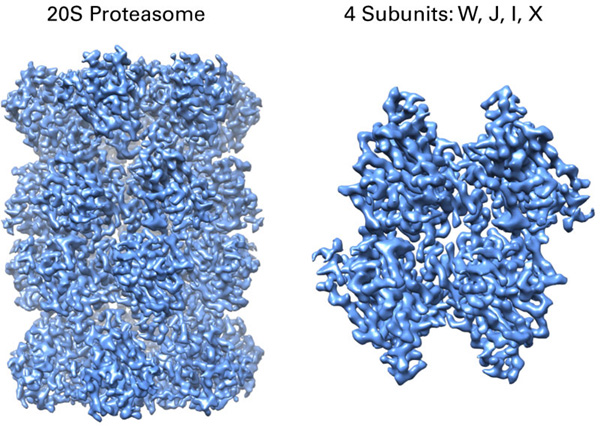
Courtesy of Alexander Myasnikov, Michael Braunfeld, Yifan Cheng, and David Agard.