Lithium Battery Research with SIMS at Tohoku University
How researchers at Tohoku University used SIMS (Secondary Ion Mass Spectrometry) in lithium battery research, to measure the lithium diffusion coefficient.
More details about this study are available in a PDF report from CAMECA.
Blue Scientific is the official distributor for CAMECA instruments in the UK, Ireland and Finland. For more information or quotes, please get in touch.
CAMECA instruments
What is dynamic SIMS?
Contact us on +44 (0)1223 422 269 or info@blue-scientific.com
Lithium Diffusion Coefficient in Battery Development
In battery and fuel cell development, it’s useful to know the lithium diffusion coefficient in the cathode material during ion transport. Thsi information can then be used to improve battery design, lifetime and optimising charge/discharge performance.
However, establishing the lithium diffusion coefficient can be challenging. Characterisation methods such as NMR and electrochemical techniques are indirect and fail to provide reliable results.
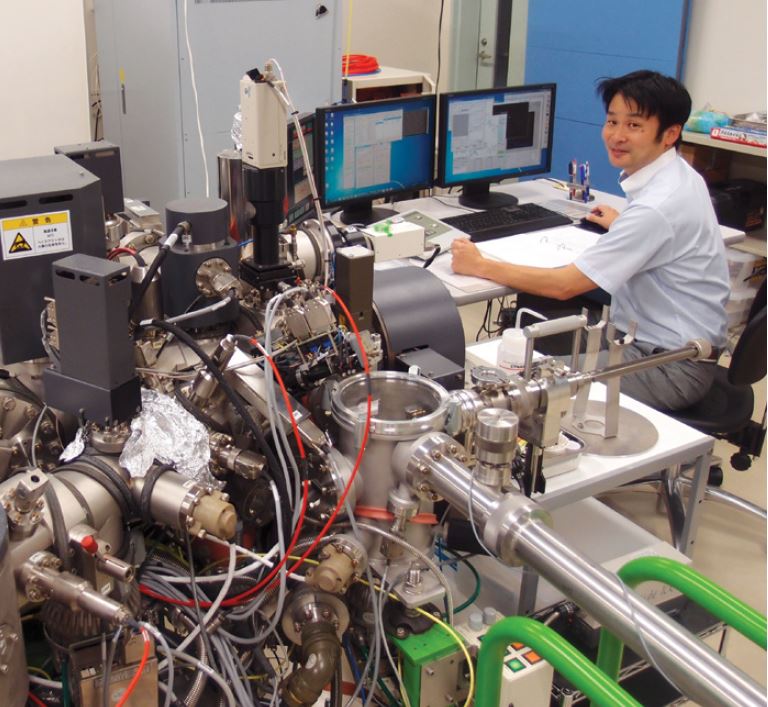
Researchers at Tohoku University used SIMS (Secondary Ion Mass Spectrometry) to precisely establish the coefficients, and gain significant insights into lithium ion behaviour.
Instrumentation
The team at Tohoku University used the CAMECA IMS 7f universal magnetic sector SIMS. This is the forerunner of the current IMS 7f-Auto:

CAMECA IMS 7f-Auto
- Measure challenging light and trace elements eg lithium.
- Excellent sensitivity, with low detection limits.
- Low background.
- Rugged and reliable.
- Superior depth/diffusion profiling.
- Versatile instrument.
The IMS 7f has a high-density primary ion beam with superior beam current stability, as well as sub-micron lateral resolution and nanometre depth resolution.
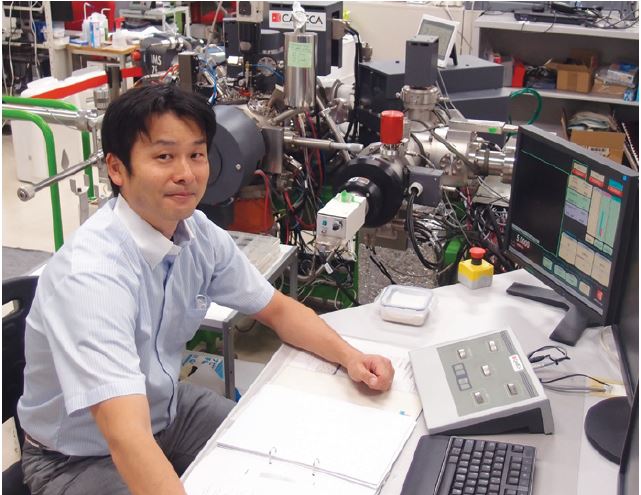
Stable Measurements
To measure the tracer diffusion coefficient, they used a combination of depth profiling and planar point analysis. This required long-term stability and optimised primary beam focusing.
The study focused on the tracer diffusion coefficient of lithium manganese oxide (LiMn2O4) thin films. The coefficient was measured using isotope ion-exchange and SIMS line analysis.
The 6Li and 7Li isotopes in the tracer exhibited the same chemical properties, so their ionisation and detection efficiencies remained almost constant. This enabled quantitative isotope ratios to be calculated from SIMS counting rates.
In contrast to TOF-SIMS, magnetic detector SIMS delivered highly reproducible data every time.
SIMS was used together with complementary data from TEM/SEM, for an extra perspective on the extremely fine-scale information.
More details about the study are available in a PDF from CAMECA.
Versatile Technique
The IMS 7f is extremely versatile. Tohoku University and researchers around the world have used it for a varied range of applications including geology, chemistry, basic physics research, and even diverse studies such as hydrogen embrittlement in steel and radioactive materials in animal horns.
More Information
To find out more about SIMS and how it could be used in your area of work, contact us for details and demonstrations.
Blue Scientific is the official distributor of CAMECA elemental and isotopic analysis instruments in the UK and Finland region. We’re available to answer all your questions – just get in touch:
Contact us on +44 (0)1223 422 269 or info@blue-scientific.com
View the CAMECA range